Eimeria stiedae life cycle
Home » Query » Eimeria stiedae life cycleYour Eimeria stiedae life cycle images are available in this site. Eimeria stiedae life cycle are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Eimeria stiedae life cycle files here. Get all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for eimeria stiedae life cycle pictures information linked to the eimeria stiedae life cycle keyword, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
Eimeria Stiedae Life Cycle. Eimeria stiedae completes its life-cycle in the bile ducts of rabbits Mykytowycz 1962. Replication takes place in the mesenteric lymph nodes before transport via the hepatic portal circulation to. Eimeria stiedae is a species of Eimeria that causes hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. Relationship between liver disorders and protection against Eimeria stiedai infection in rabbits immunized with soluble antigens from the bile of infected rabbits.

Relationship between liver disorders and protection against Eimeria stiedai infection in rabbits immunized with soluble antigens from the bile of infected rabbits. Eimeria stiedae is a species of Eimeria that causes hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. Schizogenous and gametogenous stages of the endogenous life-cycle of intestinal Eimeria spp have been found in the testes ovary swim-bladder. In this review we discuss different aspects of the life cycle and stages of Eimeria species focusing on cellular structures and organelles typical of the coccidian family as well as genus-specific features complementing some unknowns with what is described in the closely related coccidian Toxoplasma gondii. Endogenous multiplication by asexual merogony variously known as schizogony followed by sexual gamogony microgametes fertilize macrogametes producing oocysts which are excreted and undergo asexual sporogony forming sporocysts containing infective sporozoites. The oocysts are released in early unsporulated form Ou by hosts in the surroundings.
The release of _____ during schizogony causes some of the observed pathology with Eimeria bovis.
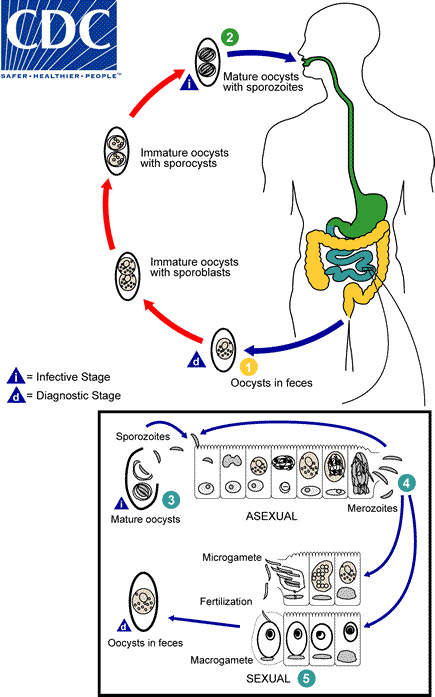
The life cycle of E stiedae is typical of Eimeria spp in that all Eimeria are host-specific and have a direct life cycle2 Oocysts are not infective until sporulation so ingestion of cecotroph feces does not result in autoinfection Ingestion of sporulated oocysts sporocysts results in release excystation of sporozoites in the duodenum Sporozoites invade the intestinal mucosa are. 2 Pathogenesis and Pathology. Eimeria stiedae is a species of Eimeria that causes hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. In this review we discuss different aspects of the life cycle and stages of Eimeria species focusing on cellular structures and organelles typical of the coccidian family as well as genus-specific features complementing some unknowns with what is described in the closely related coccidian Toxoplasma gondii. Life Cycle of Eimeria stiedae. Nature 227 304 1970.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Eimeria stiedae completes its life-cycle in the bile ducts of rabbits Mykytowycz 1962. Hanada S Omata Y Umemoto Y Kobayashi Y Furuoka H Matsui T Maeda R Saito A. What is the life cycle of Eimeria bovis. Replication takes place in the mesenteric lymph nodes before transport via the hepatic portal circulation to. The life cycle of Eimeria stiedae.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
What species does Eimeria stiedae infect. Yes the most pathogenic. Hepatic coccidiosis-Bile duct epithelium -Bile duct enlargement. The life cycle of each species is host specific and direct. Life Cycle of Eimeria stiedae.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The life cycle of each species is host specific and direct. After initial penetration of the duodenal epithelium by the sporozoites the earliest observation. The rabbits ingest sporulated oocysts. In naturally Eimeria stiedae infected rabbits. What is the life cycle of Eimeria bovis.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Eimeria stiedae is a species of Eimeria that causes hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. Eimeria stiedae completes its life-cycle in the bile ducts of rabbits Mykytowycz 1962. The exogenous phase sporogony and the endogenous phase schizogony and gametogony the initial infective unit of all eimeria spp. The rabbits ingest sporulated oocysts. Eimeria stiedae sporulated oocyst.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Eimeria stiedae completes its life-cycle in the bile ducts of rabbits Mykytowycz 1962. 2 Pathogenesis and Pathology. What does eimeria ninakohlyakimovae infect. The oocysts are released in early unsporulated form Ou by hosts in the surroundings. Eimeria stiedae sporulated oocyst.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Life cycle of Eimeria tenella. Eimeria bovis life cycle. Discussion Eimeria species are coccidian parasites of the phylum Apicomplexa. Life cycle of Eimeria stiedae. 2 Pathogenesis and Pathology.
 Source: cdc.gov
Source: cdc.gov
Replication takes place in the mesenteric lymph nodes before transport via the hepatic portal circulation to. Ingested oocysts hatch in the duodenum and sporozoites penetrate the intestinal mucosa before being transported to the liver either in the blood- stream or in macrophages in the lymphatic system. After initial penetration of the duodenal epithelium by the sporozoites the earliest observation. It was observed for the first time by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1674. Life Cycle of Eimeria stiedae.

What species does Eimeria stiedae infect. 1970 Jul 18227 5255304. Eimeria stiedae has a slightly different life cycle to the intestinal Eimeria spp. The rabbits ingest sporulated oocysts. The eimeria life cycle has basically two stages.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It was observed for the first time by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1674. Hepatic coccidiosis-Bile duct epithelium -Bile duct enlargement. What does it cause. What is the life cycle of Eimeria bovis. Goats Proliferative enteritis lower SI and LI.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Is the sporozoite stage which is a banana shaped motile cell. Eimeria stiedae is a species of Eimeria that causes hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. Numbers correlate with subsequent stages of the development. The eimeria life cycle has basically two stages. Ingested oocysts hatch in the duodenum and sporozoites penetrate the intestinal mucosa before being transported to the liver either in the blood- stream or in macrophages in the lymphatic system.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
The Eimeria life cycle has an exogenous phase during which the oocysts are excreted into the environment and an endogenous phase where parasite development occurs in. Schizogenous and gametogenous stages of the endogenous life-cycle of intestinal Eimeria spp have been found in the testes ovary swim-bladder. In this review we discuss different aspects of the life cycle and stages of Eimeria species focusing on cellular structures and organelles typical of the coccidian family as well as genus-specific features complementing some unknowns with what is described in the closely related coccidian Toxoplasma gondii. Eimeria stiedae is a species of Eimeria that causes hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. The life cycle of each species is host specific and direct.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The oocysts are released in early unsporulated form Ou by hosts in the surroundings. 2 Pathogenesis and Pathology. The release of _____ during schizogony causes some of the observed pathology with Eimeria bovis. The exogenous phase sporogony and the endogenous phase schizogony and gametogony the initial infective unit of all eimeria spp. Eimeria stiedae sporulated oocyst.

The Eimeria life cycle has an exogenous phase during which the oocysts are excreted into the environment and an endogenous phase where parasite development occurs in. Is Eimeria stiedae pathogenic. What is the life cycle of Eimeria bovis. Eimeria stiedae completes its life-cycle in the bile ducts of rabbits Mykytowycz 1962. Liver tissue was collected from two specific pathogen-.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
It was observed for the first time by Antoni van Leeuwenhoek in 1674. 1970 Jul 18227 5255304. Life cycle of Eimeria stiedae. It was observed for the first time by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1674. 2 Release of sporocysts and sporozoites along the transit in the chicken digestive system.
 Source: alchetron.com
Source: alchetron.com
PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE MeSH Terms. Life cycle of Eimeria stiedae. PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE MeSH Terms. The life cycle of each species is host specific and direct. Sporozites invade epithelial cells Sporozoites round up into trophozoites Megaschizont 1st generation schizont.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
What does it cause. The exogenous phase sporogony and the endogenous phase schizogony and gametogony the initial infective unit of all eimeria spp. 1970 Jul 18227 5255304. PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE MeSH Terms. Life cycle of Eimeria stiedae.
 Source: blog.ub.ac.id
Source: blog.ub.ac.id
Nature 227 304 1970. Eimeria stiedae has a slightly different life cycle to the intestinal Eimeria spp. Nature 227 304 1970. Life cycle of Eimeria tenella. 1 Oocyst sporulation in the environment and oral ingestion by the chicken.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Eimeria stiedae completes its life-cycle in the bile ducts of rabbits Mykytowycz 1962. The life cycle of E stiedae is typical of Eimeria spp in that all Eimeria are host-specific and have a direct life cycle2 Oocysts are not infective until sporulation so ingestion of cecotroph feces does not result in autoinfection Ingestion of sporulated oocysts sporocysts results in release excystation of sporozoites in the duodenum Sporozoites invade the intestinal mucosa are. Eimeria stiedai is considered to be one of the most important. Discussion Eimeria species are coccidian parasites of the phylum Apicomplexa. Eimeria stiedae completes its life-cycle in the bile ducts of rabbits Mykytowycz 1962.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title eimeria stiedae life cycle by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
Category
Related By Category
- Apex legends how to unlock characters
- Organismic valuing process
- Flag hey dudes womens
- What does flying the american flag upside down mean
- Queen of trash elmo
- American flag with blue stripe meaning
- Hey dude womens wendy patriotic stars and stripes
- Roland kubler now
- 365 days adrianna bartkowska
- Tyson spicy chicken patties recall